Home | Session 2 | Volcanoes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
Volcanoes
IV. Volcanic Landforms
A. Landforms from lava and ash (see Figs. 2 and 3 below)
- Volcanic mountains (Activity: topographic profiles of volcanoes)
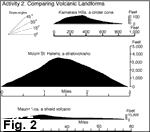
a. Shield Volcanoes (resemble warrior's shield)
- Large
- Gentle slopes
- Built primarily of flows of fluid basaltic flows
- Examples: Hawaii, Iceland, Olympus Mons (Mars)
b. Composite volcanoes (also called stratovolcanoes)
- Steep sides
- Alternating lava flows and layers of pyroclastic material
- Andesite-rhyolite (may also erupt basalt)
- Examples: Cascade volcanoes, Andes, Mt. Pinatubo
c. Cinder cones
- Relatively small
- Form by accumulation of pyroclastic fragments (cinders)
- Slopes controlled by angle of repose (30-40 degrees)
- Example: Particutín, Mexico
- Lava plateaus
Built up of multiple lava flows
Example: flood basalts of Pacific Northwest
- Caldera (Spanish for "kettle") - large depression formed by collapse of emptied magma chamber.
updated January 28, 2002
UCMP Home | What's new | About UCMP | History of Life | Collections | Subway